ElasticSearch Workflow
This article about to outline the general idea of ElasticSearch’s workflow. More precisely is how ElasticSearch handle transport request.
There are two kind of channels for network communications in ElasticSearch:
- Http Channel. It handle Http Request.
- Transport Channel. It handle Transport Request. Cluster’s communications are working in this channel.
Here we take transport channel, and http channel has a similar workflow.
Sequence Diagram
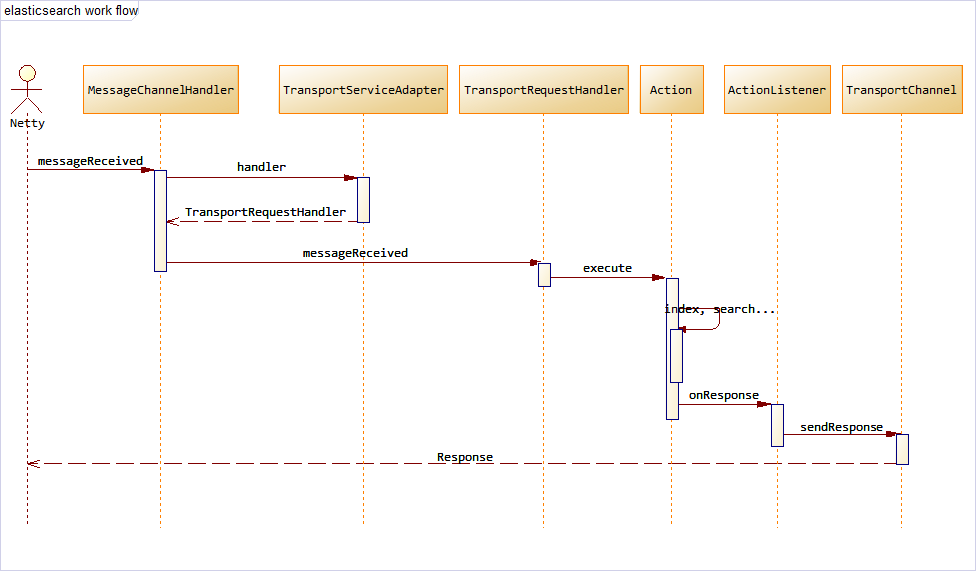
Flows
MessageChannelHandleract as a Front Controller to accept request and choose the rightTransportRequestHandler.TransportRequestHandlerthen forward request toAction.Actioninvolves other services to complete the request. Logics are actually done in this stage (indexing, searching etc.)- When it done.
ActionListenerwill tellTransportChannelto send the response back to its client.
Abstract Codes
MessageChannelHandler.messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent event) {
TransportRequestHandler handler = TransportServiceAdapter.handler(String action);
handler.messageReceived(T request, TransportChannel channel) {
Action.execute(ActionRequest request, ActionListener<ActionResponse> listener) {
// do index, search... and return ActionResponse
ActionListener.onResponse(Response response) {
TransportChannel.sendResponse(response);
}
}
}
}More general:
1/-->--\ 2/-->--\
Netty Handler Action
4\--<--/ 3\--<--/About MessageChannelHandler
ElasticSearch use Netty to handle its underline network communication. Base on Netty’s programming model one should register handlers that implement ChannelUpstreamHandler to handle request. Here in ElasticSearch MessageChannelHandler implement ChannelUpstreamHandler to do that.
NOTE: This article refers to ElasticSearch v0.4.0, APIs are no longer match exactly. Howerver, the workflow still can apply to the new version of ElasticSearch.